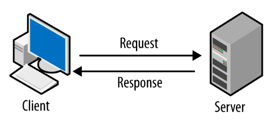
Servers
are computers with software that allows them to provide information, such as
email or web pages, to other end devices on the network. Each service requires
separate server software. For example, a server requires web server software in
order to provide web services to the network. A computer with server software
can simultaneously provide services to many different clients.
Clients
have software for requesting and displaying the information obtained from the
server.
Lists three
common types of server software:
End devices: are
either the source or destination of data transmitted over the network. In order
to distinguish one end device from another, each end device on a network is
identified by an address. When an end device initiates communication, it uses
the address of the destination end device to specify where the message should
be sent.
Intermediary
Devices: connect individual end devices to a network. They can
connect multiple individual networks to form an internetwork. These
intermediary devices provide connectivity and ensure that data flows across the
network.
Network media refers to the communication channels used to interconnect nodes on a computer network.
Metal wires
within cables: Data is encoded into electrical
impulses.
Glass or
plastic fibers within cables (fiber-optic cable): Data is
encoded into pulses of light.
Wireless
transmission: Data is encoded via modulation of specific
frequencies of electromagnetic waves.
Network
interface card (NIC): A NIC physically connects an end device to
a network.
Physical
port: A port is a connector or an outlet on a networking device
where a medium connects to an end device or another networking device.
Interface:
An interface is a specialized port on a networking device that connects to a
network. Because routers connect networks, the ports on a router are referred
to as network interfaces.
Topology
diagrams are mandatory documentation for anyone working with a
network. Such a diagram provides a visual map of how the network is connected.
There are two types of topology diagrams: physical and logical.
Small office
and home office (SOHO) Network : allow people to work from home
or a remote office. Many self-employed workers use these types of networks to
advertise and sell products, order supplies, and communicate with customers.
There are networks of varying sizes
that can be categorized in various ways, including the following:
·
Small home
networks: Small home networks connect a few computers to each
other and to the internet.
·
SOHO
networks: A SOHO network allows computers in a home office or a
remote office to connect to a corporate network or access centralized, shared
resources.
·
Medium to
large networks: Medium to large networks, such as those used by
corporations and schools, can have many locations with hundreds or thousands of
interconnected hosts.
· Worldwide networks: The internet is a network of networks that connects hundreds of millions of computers worldwide.
LAN is a network infrastructure that spans a small geographic area. LANs have specific characteristics:
- LANs interconnect end devices in a limited area
such as a home, school, office building, or campus.
- LAN is usually administered by a single organization or
individual. Administrative control is enforced at the network level and governs
the security and access control policies.
- LANs provide high-speed bandwidth to internal end devices
and intermediary devices,
WAN
is a network infrastructure that spans a wide geographic area. WANs are
typically managed by service providers (SPs) or internet service providers
(ISPs).WANs have specific characteristics:
· - WANs interconnect LANs over wide geographic
areas such as between cities, states, provinces, countries, or continents.
· - WANs are usually administered by multiple
service providers.
· - WANs typically provide slower-speed links
between LANs.
Internet is a worldwide collection of interconnected networks (internetworks, or internet for short).
Home and Small Office Internet Connection
·
Cable
connection: With this type of connection, typically offered by
cable television service providers, the internet data signal transmits on the
same cable that delivers cable television. This connection type provides a
high-bandwidth, high-availability, and an always-on connection to the internet.
· Cellular connection: Cellular internet access uses a cellphone network to connect. Wherever you can get a cellular signal, you can get cellular internet access. Performance is limited by the capabilities of the phone or other device and the cell tower to which it is connected.
· Satellite connection: The availability of satellite internet access is a benefit in areas that would otherwise have no internet connectivity at all. A satellite dish must have a clear line of sight to the satellite.
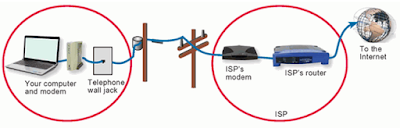
· Dialup telephone connection: This is an inexpensive option that uses any phone line and a modem. The low bandwidth provided by a dialup modem connection is not sufficient for large data transfers, although it is useful for mobile access while traveling.













No comments:
Post a Comment