kernel The portion of the operating system that interacts directly with computer hardware.
Shell The portion of the operating system that interfaces with applications and the user.
Graphical user interface (GUI) A user-friendly
interface that uses graphical images and widgets, along
with text, to indicate the information and actions
available to a user when interacting with a computer.
Command-line interface (CLI) A user interface to a computer operating system or application that depends on textual commands being entered by the user.
Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS)
Generic term for the collection of network operating
systems used by Cisco networking devices.
Firmware Permanent software programmed into ROM
memory.
Cisco Device Access Methods
- Console Term used to describe data transfer that requires the establishment of a virtual circuit.
- Secure Shell (SSH) A protocol that provides a secure remote connection to a host through a TCP application.
- Telnet A non-secure network service that supports CLI access to a remote host. It also can be used to verify the application layer software between source and destination stations.
IOS NAVIGATION
Cisco IOS software separates
management access into the following two command
modes:
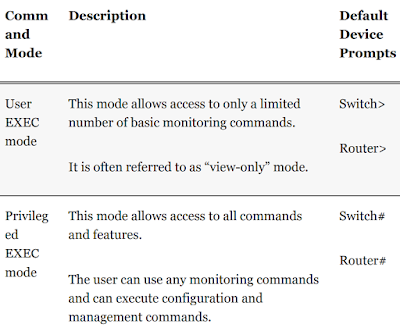
- User EXEC mode: This mode has limited capabilities but is useful for basic operations. It allows only a limited number of basic monitoring commands and does not allow the execution of any commands that might change the configuration of the device. User EXEC mode is identified by the CLI prompt that ends with the > symbol.
- Privileged EXEC mode: To execute configuration commands, a network administrator must access privileged EXEC mode. Higher configuration modes, such as global configuration mode, can be reached only from privileged EXEC mode. Privileged EXEC mode can be identified by the prompt ending with the # symbol.
IOS Command Modes
Global configuration mode A mode used to configure
global parameters or enter other configuration
submodes, such as interface, router, and line
configuration submodes.
Traceroute (tracert) A command on many computer
operating systems that discovers the IP addresses and
possibly hostnames of the routers used by the network
when sending a packet from one computer to another.
Configuration Files
Two system files store the device configuration:
- Startup-config: This is the saved configuration file that is stored in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM). It contains all the commands that will be used by the device upon startup or reboot. Flash does not lose its contents when the device is powered off.
- Running-config: This is stored in random-access memory (RAM). It reflects the current configuration. Modifying a running configuration affects the operation of a Cisco device immediately. RAM is volatile memory. It loses all of its content when the device is powered off or restarted.
IP Addresses
The use of IP addresses is the primary means of enabling
devices to locate one another and establish end-to-end
communication on the internet. Each end device on a
network must be configured with an IP address.
Examples of end devices include:
- Computers (workstations, laptops, file servers, web servers)
- Network printers
- VoIP phones
- Security cameras
- Smartphones
- Mobile handheld devices (such as wireless barcode scanners).
Switched virtual interface (SVI) A virtual interface
for which there is no associated physical hardware on the
device. An SVI is created in software. The virtual
interfaces are used as a means to remotely manage a
switch over a network. They are also used for routing
between VLANs.
CONFIGURE IP ADDRESSING
IPv4 address information can be entered into end
devices manually or automatically using Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
To manually configure an IPv4 address on a Windows
host, open the Control Panel > Network Sharing
Center > Change adapter settings and choose the
adapter. Next, right-click and select Properties to
display the Ethernet Properties dialog,Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) A
protocol used to dynamically assign IP configurations to
hosts. The services defined by the protocol are used to
request and assign an IP address, a default gateway, and
a DNS server address to a network host.